Description:
1. VPC network
Entire project’s network is in private network within 10.128.0.0/9
Each Subnet is associated with a Google Cloud region and a private RFC 1918 CIDR block for its Internal IP Address range and a gateway .
Each region has its own internal IP address so that the resources can communicate by private IP address.
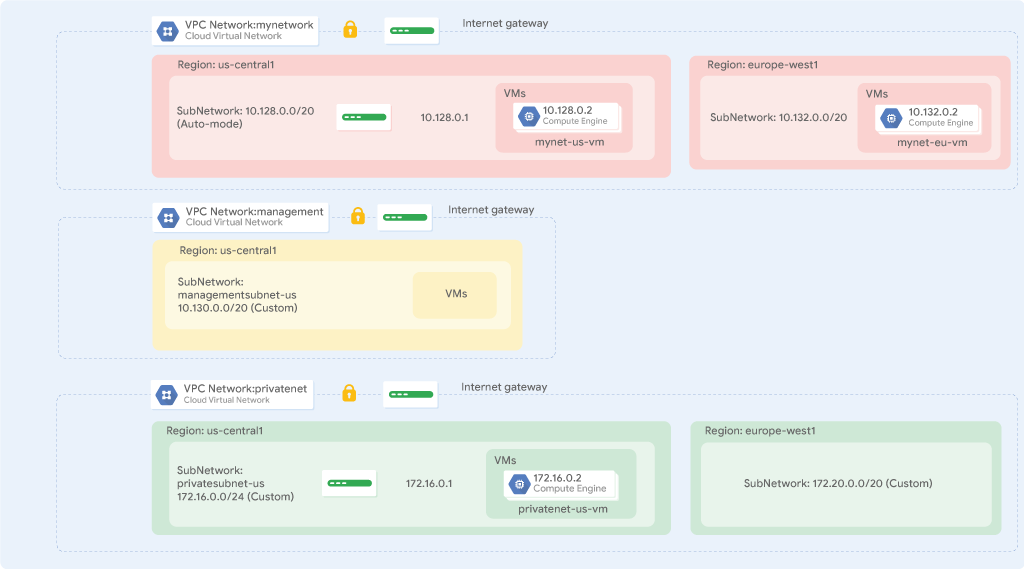
Networks in current project:
There is always a default VPC network
The network is essentially a collection of the individual IP addresses assigned to the service’s resources and the service itself.
Types of network:
default:
Preset subnet with non-overlapping CIDR blocks
Preset firewall rules
auto:
One subnet from each region is automatically created with predefined IP ranges with /20 mask
custom:
Complete control
Custom which subnet in which region using which IP range
These IP ranges cannot overlap between subnets of the same network.
can be expanded to /16 mask
Cant undo an expansion (decrease CIDR mask)
Subnets in current project:
Inside a network, you can segregate your resources with regional subnetworks.
Scope of subnets is regional, can be shared across many many zones .Can enable Private Google Access
4 IP of each subnet are reserved for networking
First, .0 for network
Second, .1 for subnet’s gateway
Last 2, …110 and …111 for 32-x bit for broadcase address
2. IP addresses
VM’s IP address
Each instance has a host name that can be resolved to an Internal IP Address
This hostname is the same as the instance name.
Cloud DNS name always points to a specific instance, no matter what the internal IP address is.
Internal FQDN for an instance that uses the format [hostname].[zone].[c].[project-id].internal
Aliases IP Ranges :
Let you assign a range of internal IP addresses as an alias to a virtual machine’s network interface.
Useful if you have multiple services running on a VM, and you want to assign a different IP address to each service.
You can configure multiple IP addresses, representing containers or applications hosted in a VM, without having to define a separate network interface.
3. Bring your own IP
By default, every network has routes that let instances in a network send traffic directly to each other, even across subnets.
every network has a default route that directs packets to destinations that are outside the network.
A route applies to an instance if the network and instance tags match.
Tags:
The route applies to all instances with any of these tags, or to all instances in the network if no tags are specified
Compute Engine then uses the Routes collection to create individual read-only routing tables for each instance.?
6. VPC network peering:
Privately connect multiple networks in google cloud regardess of projects, org
Use firewall rules to decide the allowed connections
Does not incur the network latency, security and cost drawbacks that are present when using external IP addresses or VPNs.
use this instead of interconnect
Decentralized network administration
7. Shared VPC:
Connect multiple projects in a same network within an org
allows the resources to communicate with each other securely and efficiently using internal IPs from that network.
Centralized network administration